In a world increasingly driven by conscious consumerism, materials that align with ethical, sustainable, and animal-friendly values are rising in popularity. Among them, vegan PU leather has emerged as a widely adopted alternative to traditional animal-based leather. Combining the appearance and functionality of genuine leather with a cruelty-free and often more affordable profile, vegan PU leather has become a go-to option for modern fashion, accessories, and home décor.
But what exactly is vegan PU leather? How is it made, and how does it compare to both natural leather and other synthetic materials? Whether you're shopping for a new handbag, considering upholstery options, or simply curious about sustainable materials, this guide breaks down everything you need to know — from composition and manufacturing to benefits, environmental impact, and how to tell the real (vegan) deal.
Let’s explore the story behind this material and help you make informed, ethical choices without compromising on style or practicality.

Understanding Vegan PU Leather
Vegan PU leather, short for polyurethane leather, is a synthetic material designed to mimic the appearance and texture of genuine leather. Often referred to as “pleather” (a blend of “plastic” and “leather”), it is entirely free from animal-derived ingredients, making it a cruelty-free choice. PU leather is widely used in fashion and home decor, appearing in products like handbags, shoes, jackets, and furniture upholstery. Its appeal lies in its ability to replicate leather’s aesthetic while being more affordable and easier to maintain, though its environmental impact sparks ongoing debate.
The term “vegan” in vegan PU leather emphasizes that no animals are harmed in its production. Unlike genuine leather, which is made from animal hides through a resource-intensive tanning process, PU leather is man-made, aligning with the values of vegan consumers and those concerned about animal welfare. However, not all PU leather is vegan, as some types incorporate animal-based materials, which we’ll explore later.
How Vegan PU Leather is Made
The production of vegan PU leather involves a straightforward yet customizable process that transforms basic materials into a leather-like product. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps:
Base Material Selection: The process starts with a base layer, typically a woven fabric such as polyester, nylon, or occasionally cotton. Synthetic fibers are preferred for their durability and cost-effectiveness, providing a sturdy foundation for the final product.
Polyurethane Coating: A layer of polyurethane, a versatile plastic, is applied to the base material. Polyurethane can be formulated to achieve specific properties like flexibility, water resistance, or a particular texture. The thickness and finish of this coating determine the material’s final look and feel.
Finishing Processes: After coating, the material undergoes treatments like embossing to create a leather-like grain pattern, coloring to achieve desired shades, or adding protective layers for enhanced durability. These finishes allow manufacturers to produce PU leather in a wide range of styles, from matte to glossy or even metallic.
This process results in a lightweight, flexible material that closely resembles genuine leather but is entirely synthetic, making it suitable for vegan products when no animal-based components are used.
Types of PU Leather
Not all PU leather qualifies as vegan, so it’s important to understand the distinctions:
Full-Synthetic PU Leather: This type is 100% vegan, made entirely from synthetic materials like polyurethane and a fabric base. It contains no animal products, making it the true vegan option for ethical consumers.
Semi-Synthetic PU Leather (Bicast Leather): This variant uses a base of genuine leather, often low-quality or split leather, coated with a polyurethane layer. Because it incorporates animal skin, bicast leather is not vegan. Consumers seeking vegan products must ensure they’re purchasing full-synthetic PU leather.
When shopping for vegan PU leather, always check product descriptions or labels to confirm it’s fully synthetic.
Advantages of Vegan PU Leather
Vegan PU leather offers several compelling benefits that make it a popular choice:
Affordability: Compared to genuine leather, PU leather is significantly less expensive. The lower production costs of synthetic materials versus the labor-intensive process of tanning animal hides make it accessible to a broader audience.
Ease of Maintenance: PU leather is non-porous, meaning it resists stains and spills. A quick wipe with a damp cloth is often enough to clean it, unlike genuine leather, which may require specialized cleaners and conditioners, or fabric, which can absorb liquids.
Design Versatility: Manufacturers can produce PU leather in a vast array of colors, textures, and patterns, from classic black to vibrant hues or unique finishes. This flexibility allows designers to cater to diverse fashion trends and consumer preferences.
Ethical Appeal: By avoiding animal products, vegan PU leather aligns with the values of those who oppose animal cruelty. It provides a way to enjoy leather-like aesthetics without contributing to the animal leather industry.
These advantages make vegan PU leather a practical and ethical choice for items like furniture, clothing, and accessories.
Aspect | Vegan PU Leather | Genuine Leather |
Material | Synthetic (polyurethane + fabric base) | Animal hide |
Cost | More affordable | More expensive |
Maintenance | Easy to clean with damp cloth | Requires specialized care |
Ethical Impact | Cruelty-free, vegan-friendly | Involves animal use |
環境考量
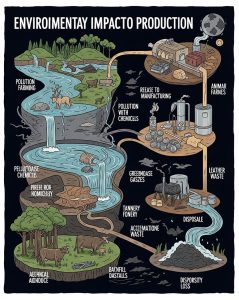
While vegan PU leather is celebrated for its ethical benefits, its environmental impact is a subject of debate. Here are key points to consider:
Non-Biodegradability: As a plastic-based material, PU leather does not break down naturally. When discarded, it can persist in landfills for centuries, contributing to long-term environmental pollution.
Chemical Usage: The production of polyurethane involves chemicals that, if not properly managed, can harm the environment or human health. Manufacturing processes may release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other pollutants.
Durability Concerns: While PU leather is durable for everyday use, it typically doesn’t last as long as genuine leather. Over time, it may crack, peel, or fade, leading to more frequent replacements and increased waste.
Energy Consumption: Producing PU leather requires energy, often from non-renewable sources, adding to its carbon footprint.
On the other hand, some argue that PU leather’s environmental impact is lower than that of genuine leather, which involves resource-intensive animal farming, water-heavy tanning processes, and chemical waste from tanneries. The debate is complex, and newer vegan leather alternatives made from plant-based materials like pineapple leaves, cork, or mushroom roots are gaining attention for their potentially lower environmental impact. For now, consumers must weigh these factors when choosing vegan PU leather.
How to Identify Vegan PU Leather
To ensure you’re purchasing vegan PU leather, use these practical identification methods:
Check Labels: Look for terms like “PU,” “polyurethane,” “faux leather,” or “vegan leather” on product tags or descriptions. Avoid items labeled simply “leather” or “genuine leather,” as these indicate animal-derived materials.
Examine Texture: Genuine leather has a natural, uneven grain with visible pores and imperfections. Vegan PU leather tends to have a smoother, more uniform surface that may feel slightly plastic-like or sticky.
Smell Test: Real leather has a distinct, earthy scent, while PU leather often has a chemical or plastic odor, especially when new. Some manufacturers mask this with artificial scents, so combine this test with others.
Water Test: Place a few drops of water on an inconspicuous area. Genuine leather absorbs water, often darkening slightly, while PU leather repels it, causing water to bead up or roll off.
Price Check: If a “leather” product is unusually affordable, it’s likely PU leather, as genuine leather commands a higher price due to its production costs.
Combining these methods ensures greater accuracy, as high-quality PU leather can closely mimic genuine leather.
Identification Method | Vegan PU Leather | Genuine Leather |
Label | “PU,” “Faux,” “Vegan Leather” | “Genuine Leather,” “Real Leather” |
Texture | Smooth, uniform, plastic-like | Natural grain, pores, imperfections |
Smell | Chemical or plastic-like | Earthy, natural |
Water Test | Repels water | Absorbs water |
Price | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Caring for Vegan PU Leather
Maintaining vegan PU leather is straightforward due to its non-porous nature. To clean, wipe the surface with a damp cloth and mild soap for tougher stains. Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners, as they can damage the polyurethane coating. Store PU leather items away from direct sunlight to prevent fading or cracking. Unlike genuine leather, PU leather doesn’t require conditioning, making it a low-maintenance option.
總結
Vegan PU leather is a significant step forward in ethical fashion, offering a cruelty-free alternative to traditional leather. Its affordability, ease of maintenance, and design versatility make it a practical choice for a wide range of products, from fashion accessories to furniture. However, its plastic composition raises environmental concerns, as it’s non-biodegradable and involves chemical-heavy production. As the demand for sustainable materials grows, innovations in plant-based vegan leathers are emerging, but PU leather remains a popular option for those balancing ethics and practicality. By understanding its benefits and limitations, consumers can make informed choices that align with their values, supporting both animal welfare and environmental consciousness.